Improving Mobility.
Does human intervention hinder or help?A leading panel of experts in small animal physiotherapy and rehabilitation, surgery, nutrition, and human obesity, met at the Iams Clinical Nutrition Symposium on February 10th 2006 in Montreux, Switzerland. At the centre of the discussion was how human intervention can positively influence mobility in companion animals, and how dogs could actually help improve the lifestyle of overweight humans to help facilitate weight loss and improve human mobility.
Key findings from the expert panel include;up to 44% of dogs and up to 35% of cats are overweight or obese
it is estimated that as many as 20% of dogs suffer from osteoarthritis and 34% of cats suffer from joint problems which can affect their mobility
weight loss is an important factor for improving mobility
cats and dogs are predisposed to trauma of the limbs due their lifestyle
over the last 10 years there has been dramatic advancement in surgical management techniques to improve mobility
total hip and elbow replacements are available to give pain free mobility
animals with orthopaedic disorders can get into a vicious cycle of decreased daily exercise and increased weight gain
combining weight loss and physiotherapy significantly improves existing lameness and mobility
owners are very important for any implementation of physiotherapy and rehabilitation regimes to help improve patientsÂ’ mobility
the last two decades has seen a rapid, world-wide spread of mobility-related diseases in humans, even in relatively poor countries
mobility of humans has been reduced due to changes in our lifestyle and eating habits
dogs offer an unique opportunity to help encourage overweight humans to exercise more and improve their mobility
Read the REPORT.
List of proceedings:Proceedings Copyrights © 2006
The Iams Company
47. Route de Saint-George
CH-1213 Petit-Lancy 1
Geneva
Switzerland
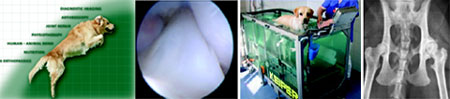
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING OF ORTHOPAEDIC PROBLEMS
IN SMALL ANIMALS: A PRACTICAL GUIDE, Professor Dr. Henri van Bree, DVM, PhD, DipECVDI, DipECVS
DIAGNOSTIC AND SURGICAL ARTHROSCOPY IN DOGS, Dr. Jean-François Bardet, DVM, MS, DipECVS
STATE OF THE ART JOINT REPAIR IN VETERINARY MEDICINE, Professor Dr. Ulrike Matis, Prof. Dr. med. vet, Dr. med. vet. habil (PhD), DipECVS
THE ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENT: CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT, PHYSIOTHERAPY AND REHABILITATION, Barbara Bockstahler, DVM, FTA Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
MAXIMISING MOBILITY WITH NUTRITION, Dr. Daniel Carey, DVM und Dr. Allan Lepine, PhD
CAN CANINE MOBILITY BENEFIT HUMAN HEALTH?, Erik Hemmingsson, PhD
HUMAN MOBILITY – BENEFITS AND LIMITATIONS OF TOTAL JOINT REPLACEMENT IN THE HIP AND KNEE, Professor Dr. Volkmar Jansson, Prof. Dr. med, Dipl.-Ing
More information can be found at www.eukanuba-scienceonline.com

|